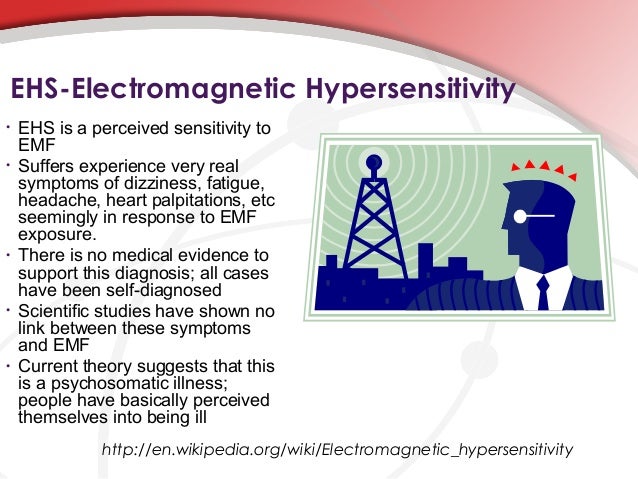
The sensitivity to electromagnetic fields (EMF sensitive) refers to a state in which a person has a strong sensitization to the electromagnetic fields that surround him. The condition isn't limited to environments in which there is no electrical current, but it can affect those who have an open circuit, or who are exposed to electromagnetic fields for prolonged durations of time. electromagnetic hypersensitivity syndrome in Dallas has a thorough understanding of the factors that cause EMF sensitivity, and can help patients treat their symptoms. The center has the ability to perform tests to determine whether an individual is susceptible to EMF exposure. This can be accomplished using new technology that measures heart rate variation.
I.E.-EMF sensitivity is a sign of emf exposure
Electromagnetic pollution and its magnetic fields that result from it are a factor in the development of a variety of illnesses. The symptoms are often difficult to identify and some individuals have reported a wide variety of symptoms. These may be a result of pre-existing conditions or an ailment caused by the prospect of exposure to large amounts in electromagnetic field. Regardless of the cause the symptoms can be debilitating for people who experience them. Despite this, the scientific community is still not certain of how prevalent the IEI-EMF sensitive syndrome is, and the extent to which it is widespread.
It is not a symptom of electrohypersensitivity
While the symptoms of electrohypersensitivity and EMF sensitivity are similar, there are some key differences. Electromagnetic hypersensitivity is often misunderstood, and symptoms can vary widely. It is essential to obtain a proper diagnosis to understand the root cause and possibilities for treatment.
It isn't a symptom of EHS
Although EMF sensitivity is not a defining characteristic of EHS however, it is frequently related to the disorder. In fact, some studies suggest that the condition may be related to environmental and genetic causes rather than a particular physical condition. Despite this, more research is needed to make definitive conclusions.
It can be confusing
The signs of EMF sensitivities can be confusing. A majority of EHS sufferers don't believe that their symptoms are due to a particular source. They seek medical treatment however are unable to get a definitive diagnosis. The result is that they could be suffering from some sort of mental disorder, and leads to an increase in feelings of anxiety and helplessness.
It can be scary
The effects of electromagnetic fields, also known as EMFs, can be terrifying. Many people have reported experiencing uncomfortable symptoms after exposure to these fieldsthat originate from devices like Wi-Fi routers and mobile phones. emf sensitivity may vary in severity, however in the most severe cases, people are forced to stay away from electric devices and fluorescent lighting. In extreme instances, those suffering may be forced to withdraw from the world of modernity, living in isolated communities that are known as "EMF-free areas".
electromagnetic hypersensitivity symptoms may aid in the production of melatonin.
The most important hormones in the body Melatonin, one of the most important hormones in the body, is synthe in the pineal gland. It plays a role in a variety of biological functions, such as the regulation of circadian rhythm. However, its role as a factor of protection in the face of nonionizing electromagnetic field has been questioned, largely due to inconsistency in results from different studies. To date, our knowledge of the hormone's protective mechanisms is mostly based on our understanding of the mechanism through which it acts to shield your body from the oxidative stress produced by RF/ELF exposure.
It can help with changes in the autonomic nervous system.
Numerous studies have shown that EMF sensitivities can impact the nervous system of autonomic control. People suffering from the condition may experience altered autonomic responses and may experience digestive issues. Some patients have problems digesting food correctly or be ill when they eat a smaller amount. Other patients may notice changes in body temperature or are suffering from heat intolerance. These conditions are usually secondary to other health conditions, such as diabetes.
